NVIDIA Is Defining the Future of Shared KV Cache—WEKA Provides the Adoption Roadmap


TL;DR NVIDIA’s Inference Context Memory Storage platform (ICMS) defines shared KV cache as foundational inference infrastructure. WEKA provides the pragmatic adoption roadmap—delivering immediate gains on existing systems, scaling to pooled architectures, and enabling a smooth transition to ICMS-native deployments.
Shared KV Cache as Foundational Inference Infrastructure
With NVIDIA’s Inference Context Memory Storage platform (ICMS), NVIDIA is articulating how modern inference systems are meant to be built. As inference moves into the agentic era—defined by long context, multi-turn interactions, and high concurrency—KV cache can no longer be treated as a transient, GPU-local detail. It becomes foundational to system behavior.
This is not a shift driven by theory or abstraction. It reflects how inference already behaves at scale:
- Context persists across turns and sessions
- Concurrency causes state to accumulate faster than on-package memory can sustain
- GPU efficiency is determined by how context is retained, accessed, and reused
ICMS captures these realities by defining shared KV cache as part of the inference infrastructure itself—something designed, managed, and scaled deliberately, rather than handled implicitly inside individual runtimes or nodes. In doing so, NVIDIA is not adding complexity to the stack; it is bringing clarity and structure to a core requirement of production inference systems.
Adoption in Real-World Environments
ICMS defines the architectural end state for shared KV cache and establishes the direction inference systems are moving toward. Translating that architecture into production environments requires a practical transition that accounts for how systems are built and operated today.
Most environments must integrate this direction within existing constraints, including:
- Deployed GPU servers and established inference software stacks
- Requirements for deployment velocity, stability, and operational risk management
- Near-term economics and hardware availability
WEKA’s NeuralMesh provides that adoption roadmap—enabling teams to realize immediate improvements on current infrastructure while progressively aligning system behavior with ICMS-native shared-context architectures.
NVIDIA Is Defining the Future of Shared KV Cache—WEKA Provides the Adoption Roadmap
NVIDIA’s ICMS platform, together with NVIDIA BlueField®-4, defines a clear architectural destination for inference systems: shared KV cache as first-class infrastructure. ICMS defines this architectural end state for shared KV cache and establishes the direction inference systems are moving toward.
Translating that architecture into production environments requires a practical transition that accounts for how systems are built and operated today.
Most environments must integrate this direction within existing constraints, including:
- Deployed GPU servers and established inference software stacks
- Requirements for deployment velocity, stability, and operational risk management
- Near-term economics and hardware availability
Real environments must balance existing software stacks, deployment velocity, and near-term economics. WEKA is designed to help customers move toward NVIDIA’s vision through a pragmatic, staged roadmap—delivering value at every step.
These three architectures represent an adoption path to ICMS for every customer.
Stage 1: Backward-Compatible KV Cache Offload (Start Where You Are)
Most customers begin with existing GPU inference stacks that were never designed for shared context memory.
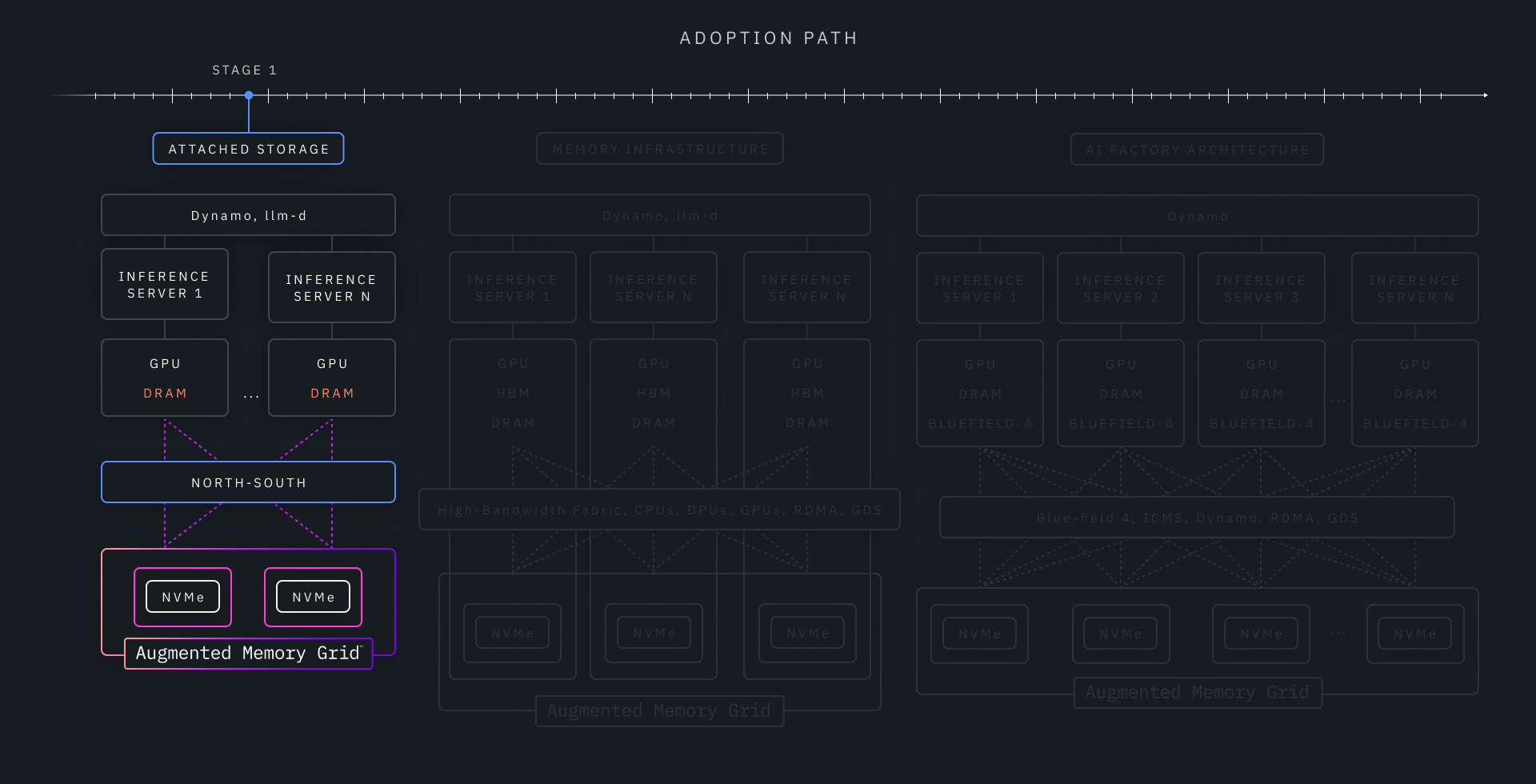
In this stage, KV cache capacity is extended beyond GPU HBM using familiar North–South access paths and standard interfaces (such as POSIX or NFS). This allows customers to relieve HBM pressure, improve utilization, and support larger or more concurrent contexts without changing inference runtimes or operational tooling.
This stage prioritizes:
- Immediate benefit on existing systems
- Minimal disruption
- Full backward compatibility
It is intentionally incremental—a fast on-ramp.
Stage 2: Optimized High-Bandwidth Fabrics for Fleet-Scale Efficiency (Run on Your GPU Servers Today)
As inference fleets grow, economics become the dominant constraint. Sustained concurrency, long-context sessions, and high utilization expose the inefficiencies of purely node-local or traditional designs.
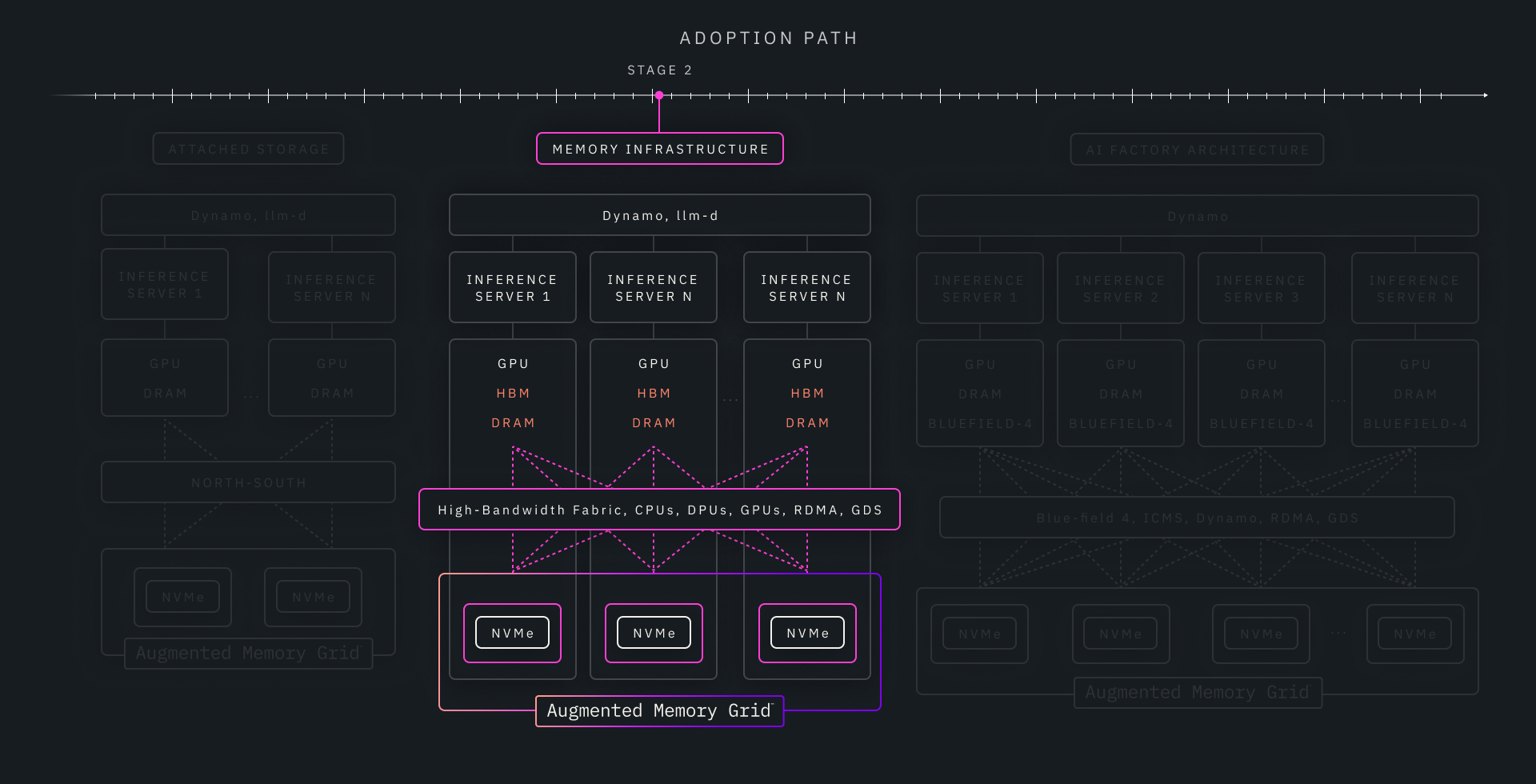
In this stage, customers adopt an optimized solution over higher-bandwidth network fabrics, enabling KV cache to be pooled and reused across GPU servers. Context begins to behave like shared infrastructure, accessed over these higher-bandwidth paths that are designed for throughput, predictability, and reuse.
Crucially, this architecture:
- Runs on GPU servers available today
- Delivers significantly better performance-per-dollar at scale
- Improves utilization by decoupling context capacity from individual nodes
This stage captures most of the economic upside of shared KV cache before full ICMS deployment.
Stage 3: ICMS Adoption—Shared KV Cache as Platform Infrastructure (The Future of Shared KV Cache)
This is the architecture NVIDIA is defining with ICMS and BlueField-4.
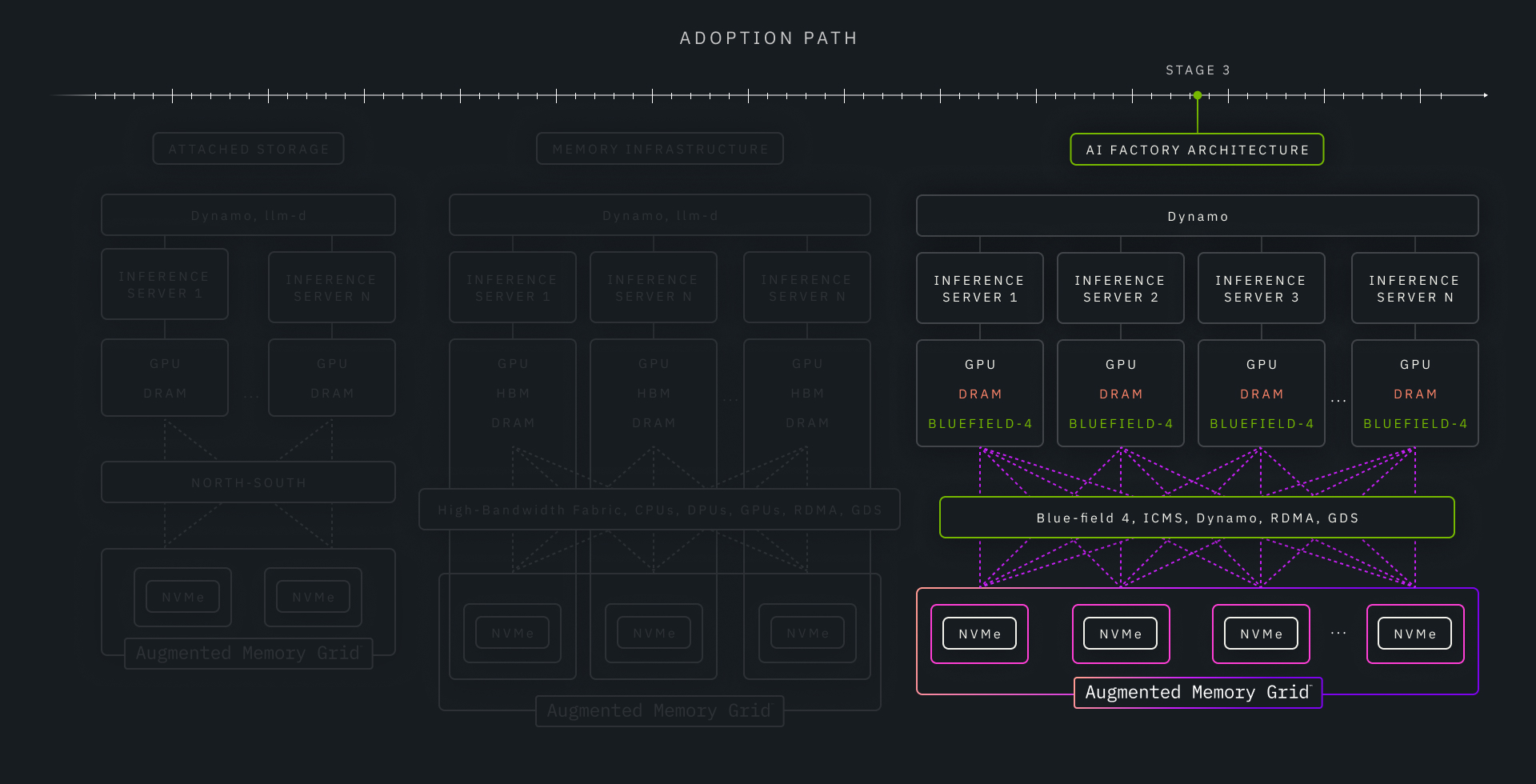
At this stage, KV cache is fully treated as shared, managed infrastructure, decoupled from GPU memory and orchestrated independently of inference execution. Context placement, eviction, isolation, and reuse become platform-level concerns rather than application-level optimizations.
This model delivers:
- Maximum context reuse
- Predictable tail latency under extreme concurrency
- The best long-term economics for large-scale inference fleets
It represents the destination architecture for inference systems built around shared context memory.
NVIDIA Defines the Future. WEKA Enables the Journey.
NVIDIA is defining ICMS for the agentic era, establishing a shared KV cache as a foundational element of inference infrastructure. We’re enabling customers to begin their journey today, by delivering immediate gains on existing systems and unlocking fleet-scale efficiency on GPU servers available today and tomorrow.
This is how customers execute a roadmap toward the future NVIDIA has defined. Read more about how we’re solving some of the toughest challenges with NVIDIA today, here.